SOC + IA: Discover the Acronyms and their joint Magic
What do they mean? How is AI transforming the SOC?
Autores


TABLE OF CONTENTS
1- Introduction
2- What is Artificial Intelligence (AI)?
2.1- Difference between AI and ML (Machine Learning)
2.2- Types and current status of AI
2.3- Short-term projections (2 years)
2.4- Importance of AI in security (General)
3- What is a Security Operations Center (SOC)?
3.1- Functions of a SOC
3.2- Advantages of AI in a SOC
3.3- Examples of AI in SOCs
4. Additional resources and recommended readings
5. Glossary of terms
CONTENTS
1- Introduction
Surely the letters “I” and “A” ring a bell, or AI in English, if they don't ring a bell, it looks like you're not in the loop, because they stand for artificial intelligence.
So what's that? In this post, we're going to explore what AI is, its characteristics, and where we are today.
We will also look at how AI is applied in different areas and, especially, how it is aligned with cybersecurity.
2- What is Artificial Intelligence (AI)?
The European Commission defines it as software (and possibly also hardware) systems designed by humans that, faced with a complex objective, act in the physical or digital dimension:
Perceiving their environment, through the acquisition and interpretation of structured or unstructured data.
Reasoning about knowledge, processing the information derived from this data and deciding the best actions to achieve the given objective.
In simple terms:
Generative artificial intelligence (AI) is a technology that creates new content from large amounts of data.
It is like a digital brain that learns from millions of examples to create something unique. It is important to understand how AI works because it is here to stay and will continue to evolve.
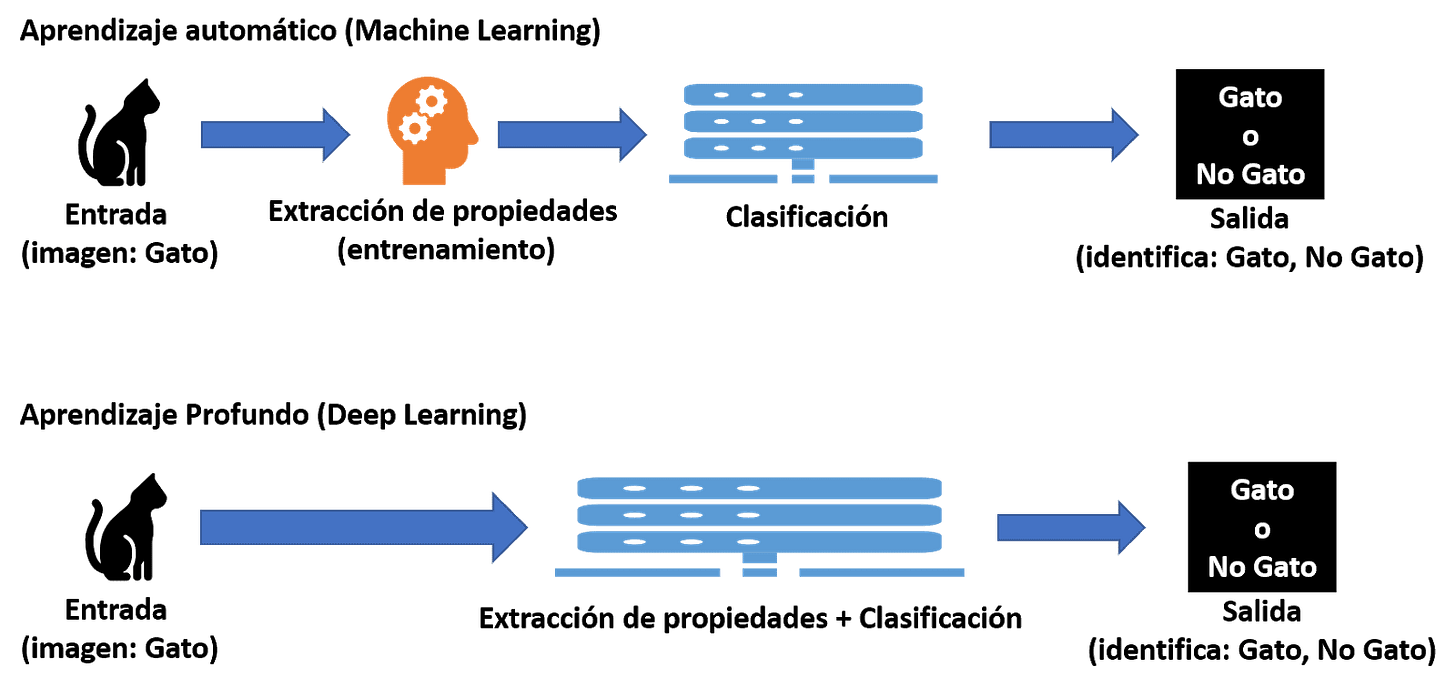
2.1- Difference between AI and ML (Machine Learning)
Deep learning, which is what today's AI uses, is an evolution of Machine Learning.
While machine learning requires some human supervision, deep learning can work more autonomously, solving complex problems with less human intervention.
2.2- Types and current status of AI
AI is classified according to its ability to mimic human characteristics. Currently, there are three stages:
Narrow artificial intelligence (ANI): focuses on specific tasks, performing repetitive work in an environment predefined by their creators. They have no learning capabilities or self-awareness, but can match or even surpass human efficiency.
Common examples include virtual assistants such as Siri and Alexa, and voice recognition systems.
Artificial general intelligence (AGI): also known as strong AI, this stage will be reached when AI can understand, learn and perform any task that a human can do.
Although a fully functional one has not yet been developed, there is already much discussion about its potential implications.
Superintelligent artificial intelligence (ASI): This hypothetical stage would be reached when AI far exceeds human capabilities in all aspects. The implications of this are cause for debate and concern.
Remember the movie Terminator and SKYNET? We don't want that to become a reality, do we?
We are currently in the ANI stage, but this is evolving very, very fast.
2.3- Short-term projections (2 years)
Although AI is surrounded by a lot of marketing, its use is expanding rapidly in a number of areas:
Have you noticed that every time you submit a support ticket or call your service provider, it is more common to be answered by a machine rather than a person?
This trend will continue to increase and they will get smarter and smarter.
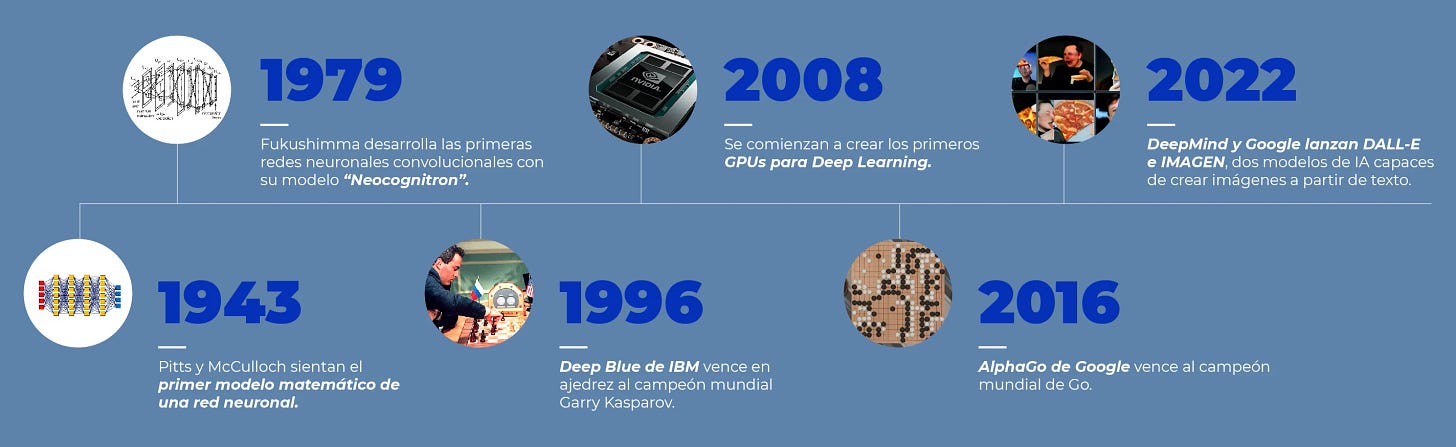
Although we don't have a crystal ball to predict the future, we would like to show you the following image to show you how fast we are moving forward:
In just a few years, we have achieved advances that used to take decades or even centuries.
Can you imagine what we could achieve in the next few years?
What about in a decade? We are at the beginning of something very big.
2.4- Importance of AI in Safety (General)
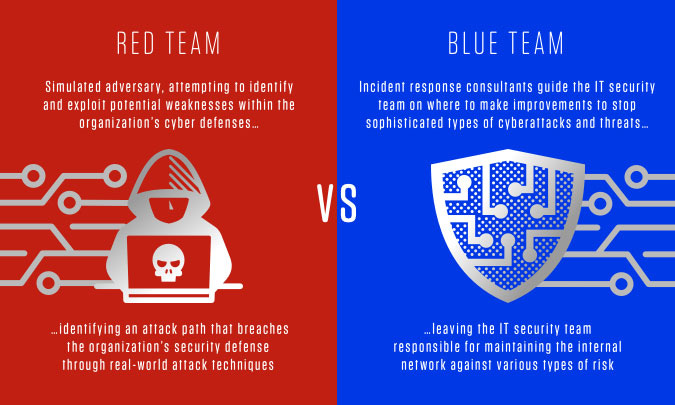
Artificial intelligence (AI) is fundamental to improving digital security. Its application can be approached as follows according to the different teams:
Red Team (Attackers): This team is responsible for identifying and exploiting vulnerabilities in an organization's systems to improve its security.
AI helps us to find vulnerabilities semi-automatically or automatically and to perform penetration tests more efficiently.
This allows us to identify and correct potential weaknesses before attackers can exploit them.
Blue Team (Defenders): This team is responsible for protecting the organization's systems against potential attacks.
AI improves our ability to detect and respond to security incidents.
It can analyze large volumes of data in real time to identify suspicious behavior, alerting and assisting security analysts, facilitating a fast and effective response.
3- What is a Security Operations Center (SOC)?
A Security Operations Center (SOC) is a team specialized in monitoring and protecting an organization's digital infrastructure.
Its main objective is to detect, analyze and respond (CSIRT) to security threats in real time, ensuring that the network and data are kept secure.
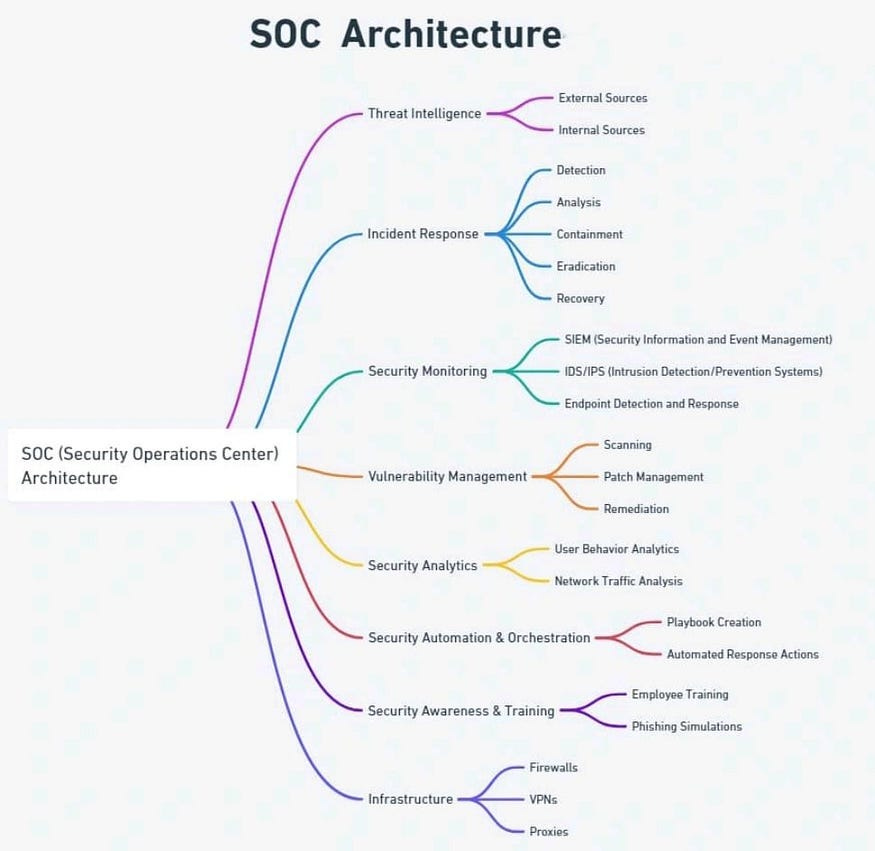
3.1- Functions of a SOC
The key functions of a SOC include:
Continuous monitoring: Monitor the organization's network and systems 24/7 to detect suspicious or anomalous activity.
Threat detection: Use advanced tools such as SIEM to correlate and analyze logs for signs of threats.
Incident analysis: Investigate security alerts and events to determine their nature and severity.
Incident response (CSIRT): Implement mitigation and response measures to neutralize threats and minimize their impact.
Vulnerability management: Identify, assess and remediate or mitigate vulnerabilities in the organization's systems and applications.
Threat intelligence: Gather and analyze information on new threats and cybersecurity trends to improve the organization's defenses.
Reporting and audits: Generate regular reports on security status and SOC activities for senior management and auditors.
Regulatory Compliance: Ensure that SOC security policies and practices comply with applicable regulations and standards.
They are usually organized in different levels to efficiently manage alerts and incidents:
N1: First level of analysis, responsible for initial monitoring and identification of basic alerts.
This level filters and classifies alerts to determine which ones need immediate attention.
N2: Second level, responsible for more in-depth investigation and management of complex incidents.
Here, detailed analysis is performed and decisions are made on the necessary corrective and response actions.
N3: Third level, specialized in advanced incident management and forensic investigation.
This level focuses on high-severity incidents that require a deep understanding of the infrastructure and the development of long-term solutions to prevent future threats.
It may also involve collaboration with external teams and the implementation of security infrastructure improvements.
3.2- Advantages of AI in a SOC
AI offers many operational advantages in a SOC:
Increased efficiency: AI processes large volumes of data quickly and accurately, optimizing log management and reducing SOC operating costs.
New use cases: AI facilitates the creation of new use cases based on specific requirements, improving detection capabilities in the infrastructure and adapting to new needs.
Reduction of false positives: By analyzing behavioral patterns and correlating data, AI differentiates between real threats and possible false alarms. This not only decreases the number of unnecessary alerts, but also adjusts detection rules for greater accuracy.
Improved decision making: AI provides recommendations based on comprehensive analysis of current and past data, suggesting the best actions to take in response to incidents.
Process automation: AI automates repetitive and routine tasks, such as daily report generation, allowing analysts to focus on more complex problems and critical incident resolution.
Threat intelligence: Provides detailed and up-to-date information on new threats and emerging trends. This intelligence allows proactively strengthening defense and adjusting security strategies based on the latest detected threats and specific characteristics of the infrastructure.
Currently, AI acts more like a co-pilot than a fully autonomous system.
Although a valuable tool, security incidents still require human critical thinking for a thorough assessment and appropriate response.
3.3- Examples of AI in SOC
To better understand how artificial intelligence (AI) improves the performance of a SOC, I recommend watching this video from my colleagues at Softeng, which shows a real test in action.
PS: I advise you to watch the whole video since they explain very interesting concepts, but if you want to go directly to a practical case of a security incident, I suggest you go to minute 8:07.
4. Additional resources and recommended reading
What is Artificial Intelligence:
https://planderecuperacion.gob.es/noticias/que-es-inteligencia-artificial-ia-prtr
ANI, AGI and ASI and the future of AI:
https://es.linkedin.com/pulse/ani-agi-y-asi-el-futuro-de-la-ia-miguel-%C3%A1ngel-trabado
The 3 stages of Artificial Intelligence: which one are we in and why many think that the third one can be fatal:
https://www.bbc.com/mundo/noticias-65617676
Demonstration of basic SIEM/SOC operation:
https://jaymonsecurity.es/master-soc-box-demo-siem-soc-2/
Which SIEM solutions offer the most advanced AI-driven machine learning and threat detection capabilities?
https://www.linkedin.com/advice/0/which-siem-solutions-offer-most-advanced-machine-h3h2f
The importance of Artificial Intelligence in cybersecurity: https://blog.conzultek.com/ciberseguridad/inteligencia-artificial-en-la-ciberseguridad
Microsoft Azure AI Fundamentals:
https://learn.microsoft.com/en-us/training/courses/ai-900t00#course-syllabus
What is artificial intelligence (AI)?
https://aws.amazon.com/es/what-is/artificial-intelligence/
Microsoft Copilot for Security:
https://www.microsoft.com/es-es/security/business/ai-machine-learning/microsoft-copilot-security
6. Glossary of terms
SOC: Abbreviation for “Security Operations Center”. Refers to a team specialized in monitoring and protecting an organization's digital infrastructure.
CSIRT: Computer Security Incident Response Team. It is a specialized group within an organization or entity, responsible for managing and responding to incidents related to the security of computer systems.
SIEM: Abbreviation for Security Information and Event Management. It is a software solution that allows the collection, correlation and analysis of security data to identify and respond to potential threats.
Artifical Intelligence (AI): Scientific discipline that deals with creating programs and mechanisms that exhibit human characteristics, such as reasoning, learning, perception and the ability to make decisions.
Cybersecurity: A set of techniques, measures and policies designed to protect digital information and computer systems against attacks, damage or unauthorized access.